Engine S/N G6X01029 Cat 3306, Gas
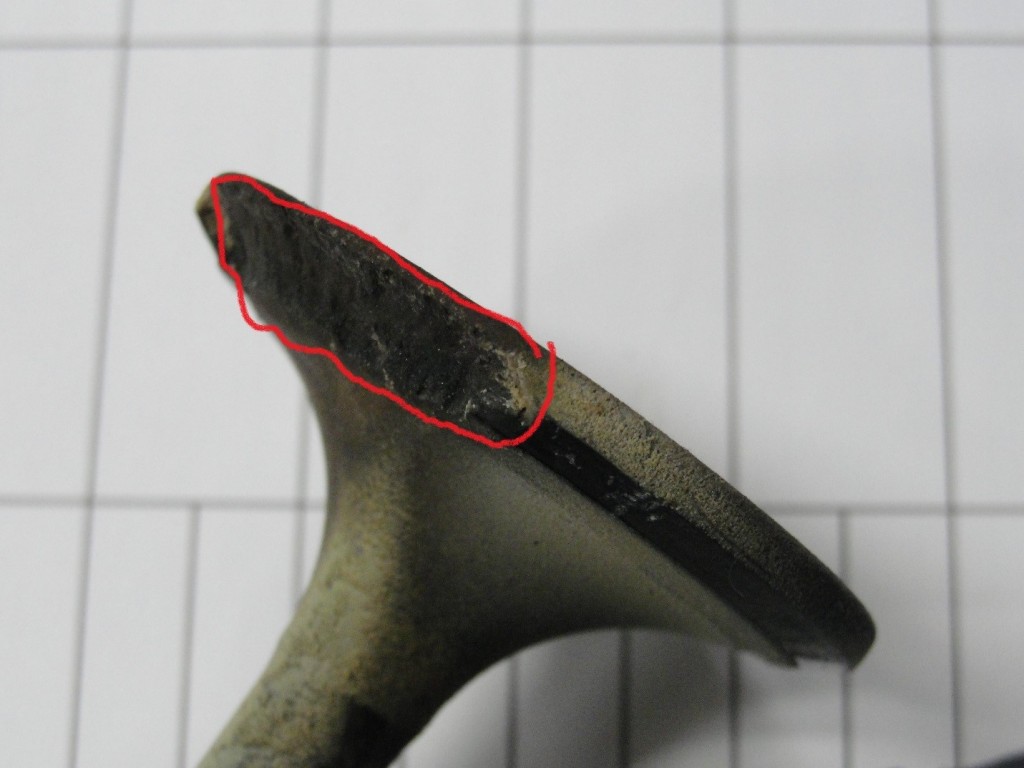
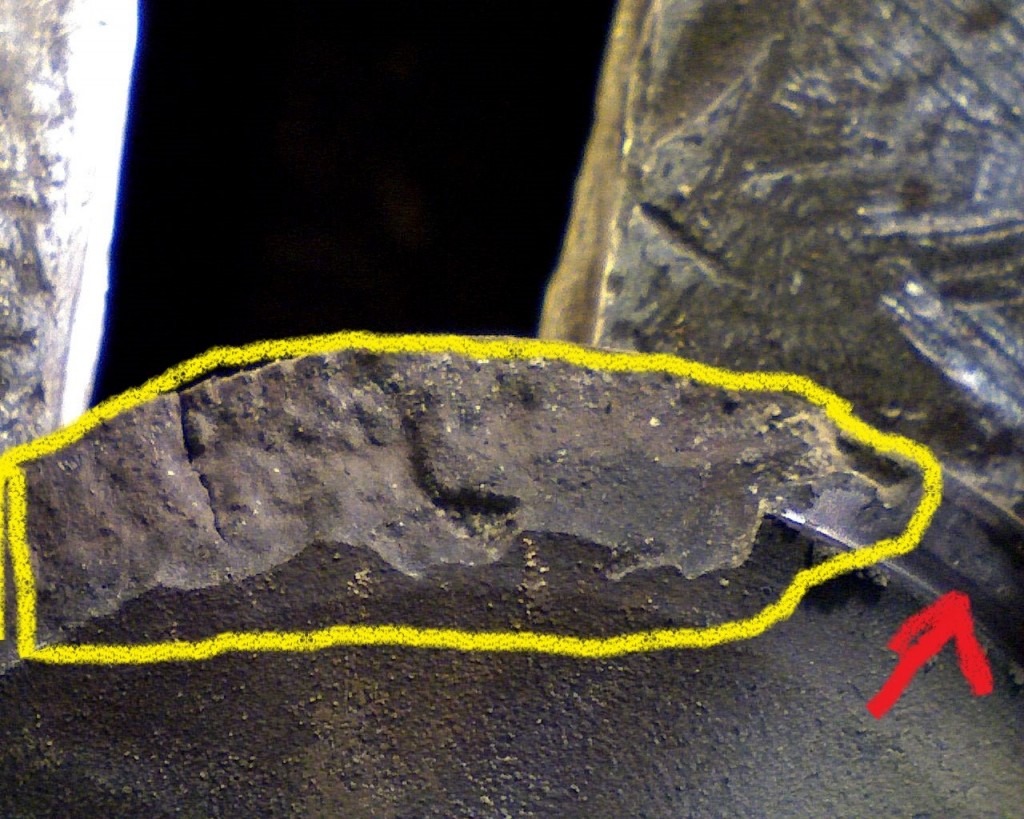
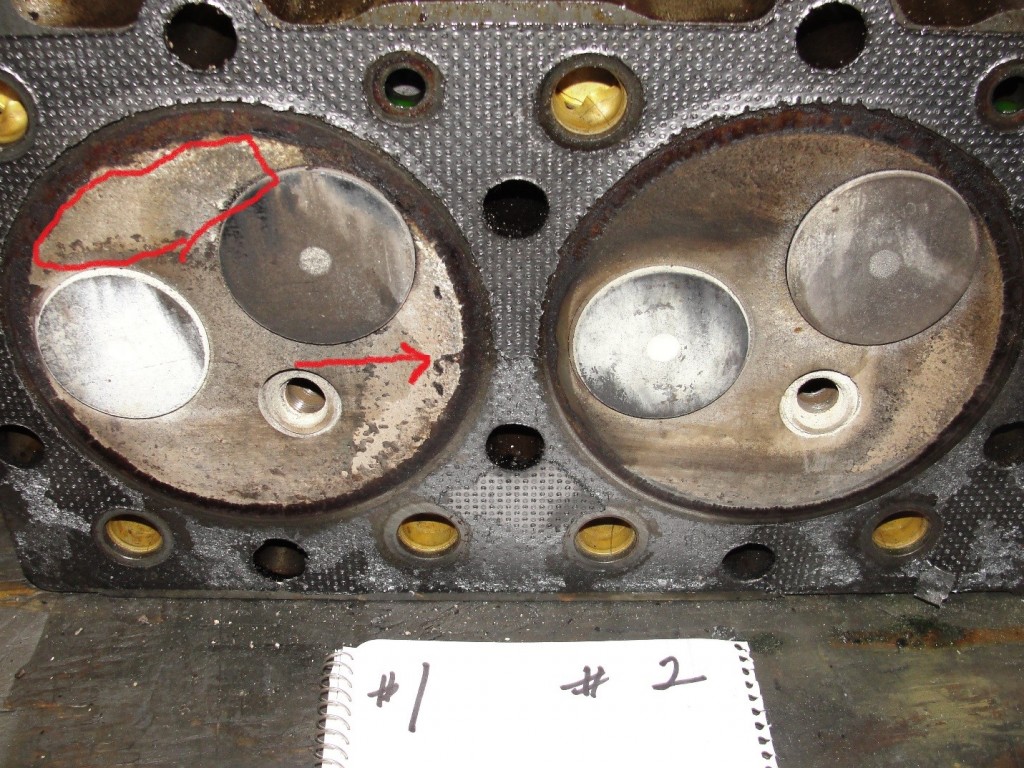
These deposits that build-up on the cylinder head, valves, valve guides, valve seats insert and pistons are solid particles that stick/cling to hot surfaces. These deposits build –up on valves face seat sealing area and valve insert seat sealing area and interferes with proper sealing of valves and promotes combustion gas leak path. Also these deposits flake off and get trapped between valve face seat sealing and valve insert seat sealing area causing a combustion gas leak path. This leak path of hot combustion gases melt valve material causing valve guttering/torching
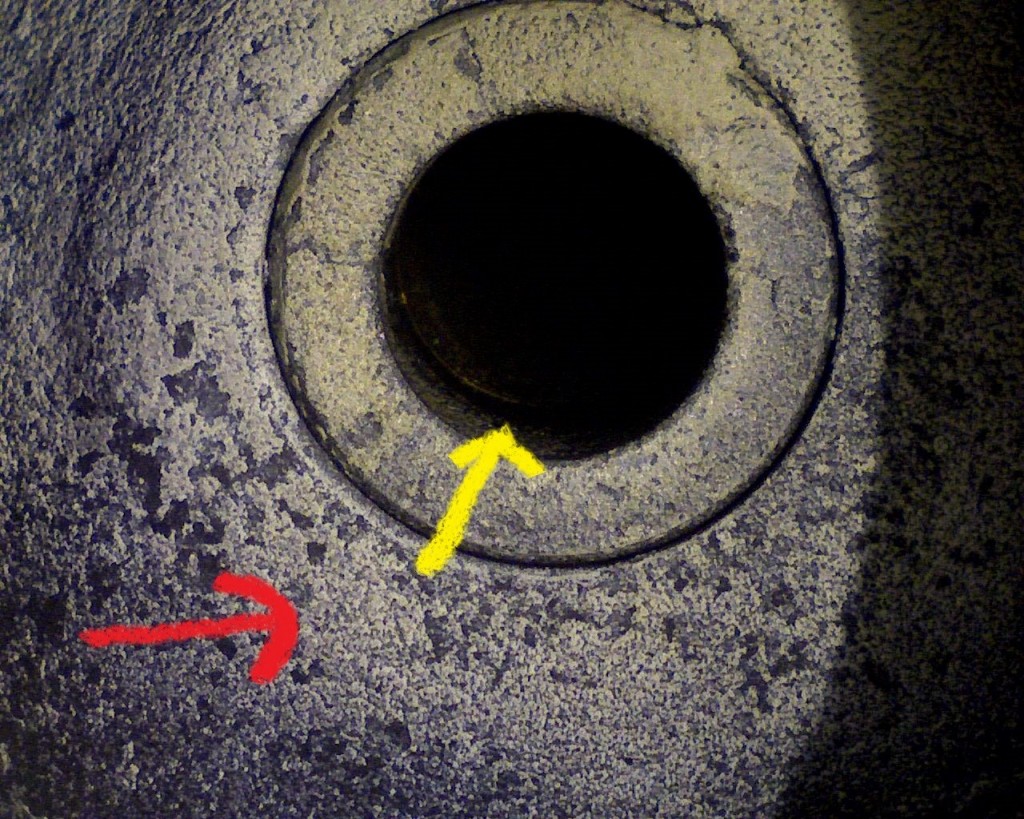
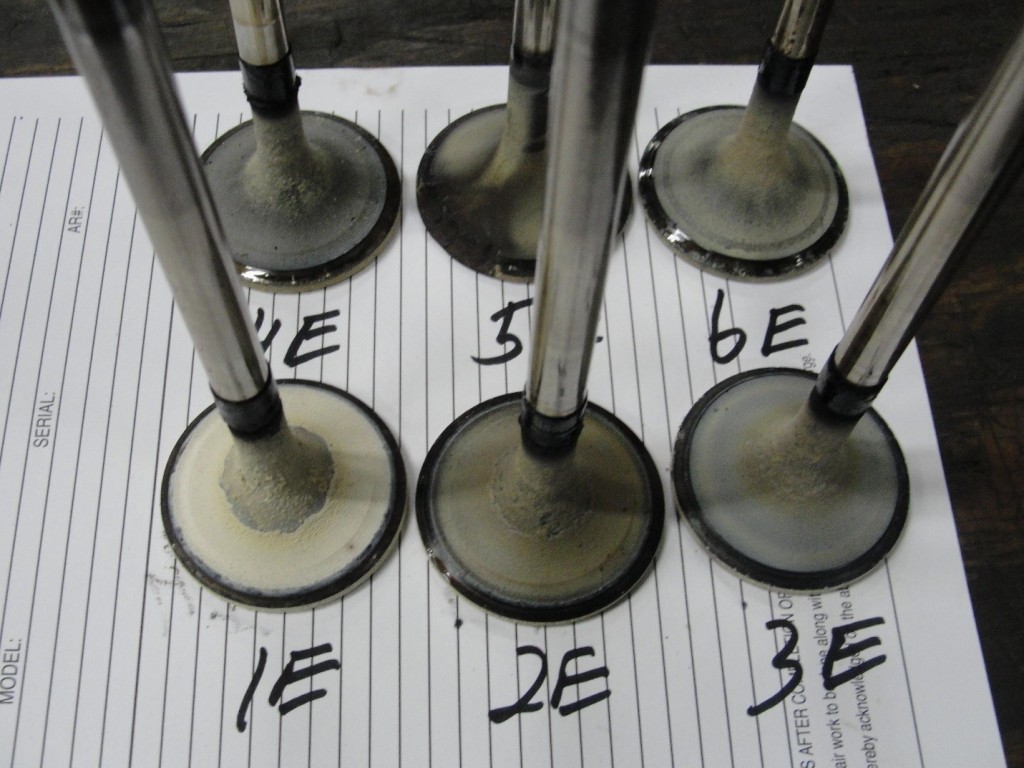
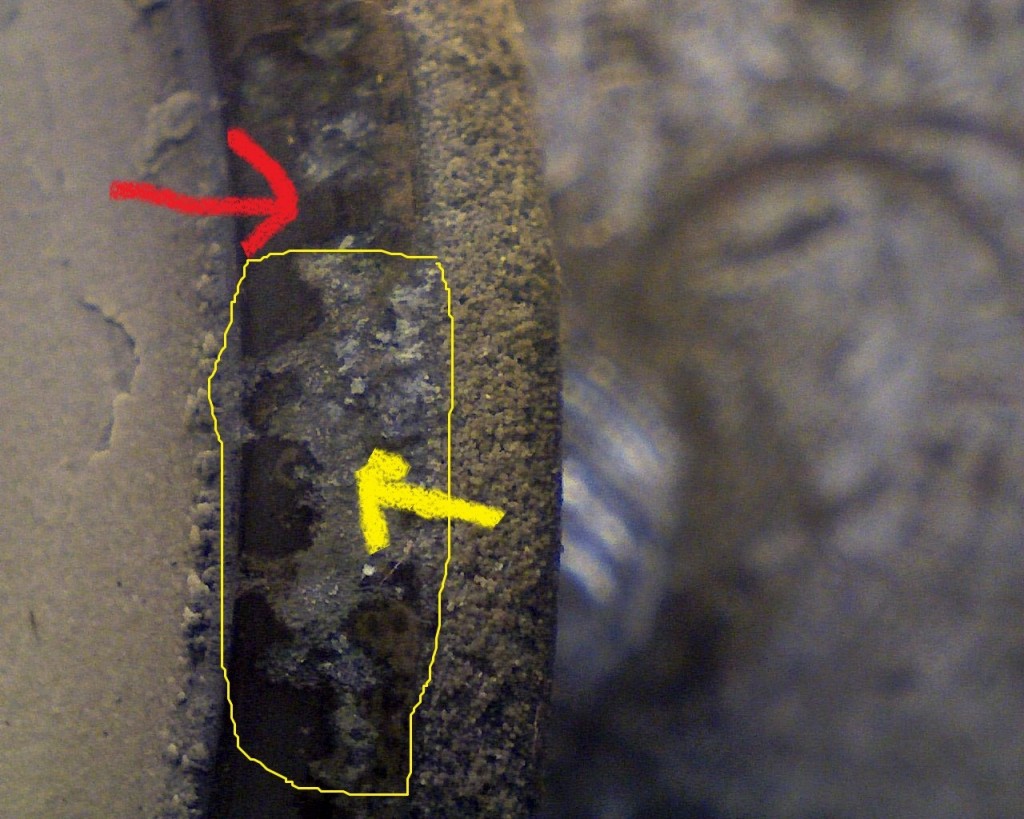





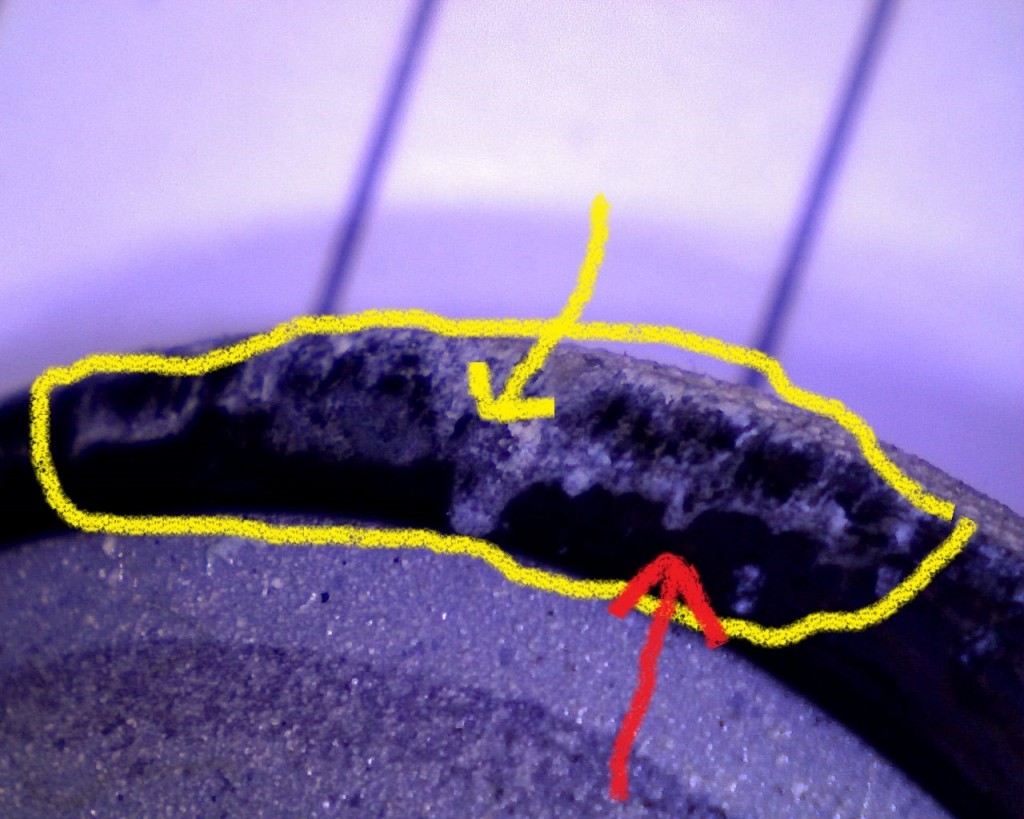








Had [SEM] scanning electron microscopy analysis of deposits on exhaust and intake valves.
Elements that were in deposits.
CA – Calcium New oil additive 1132-1384 PPM
ZN – Zinc New oil additive 290-358 PPM
P – Phosphorous New oil additive 255-311 PPM
S – Sulfur In natural gas
O – Oxygen
C – Carbon By product of combustion deposits
FE – Iron Liners and valves
CR – Chromium Valves, top piston rings, valve stem plating
NI – Nickel valves
K – Potassium New oil and airborne
NA – Sodium New oil and airborne
Deposits are due to burning excessive oil during the combustion process.
3306 engine S/N G6X01029 if this engine has not been re-rated to a new spec number operating this engine at 1250 RPM and 35% load is a concern. This engine per Cat test cell number 511 report engine is rated at 202HP @1800 RPM. A typical natural gas engine design will optimize valve lubrication at full load, but this can lead to excessive oil flow to the valves under low load conditions. Prolonged operation at low loads below the boost range of turbo can lead to increased oil consumption and a resulting build-up of deposits. Operation at low loads and low RPM causes low intake manifold pressures which can result in higher than normal oil lubrication of valves, rings and liners.
This engine cylinder head was built with no valve guide seals. With low load conditions this causes excessive oil between valve guide and valve stem.
Need to check intake manifold pressure with engine operation at its normal conditions. Per Cat natural gas 3306 engine performance data.
100% load 75% load 50%load
Manifold pressure 38.5 HG 32.3 HG 24.9 HG
Manifold pressure 18.9 PSI 15.9 PSI 12.2 PSI
Cause of valve failure is deposits between exhaust valve face seat sealing area and valve insert seat sealing area due to engine burning excessive oil in the combustion process.
